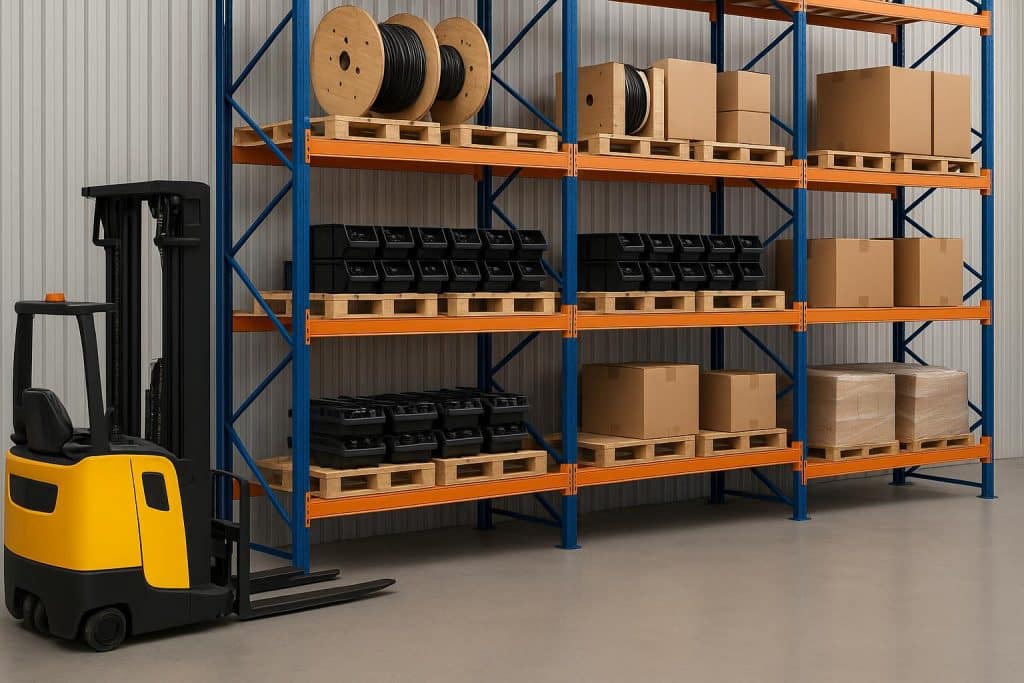
Few warehouses simply stumble upon efficiency-it’s engineered. Begin by marrying the right lifting equipment with purpose-designed storage systems, and then tune workflows, safety, and maintenance around those assets. In that regard, one of the central pieces for that approach will be leveraging an Electric Forklift fleet for predictable, low-emission material movement. Electric lift trucks reduce noise and eliminate onsite combustion emissions that enable you to reconfigure storage and operations inside enclosed facilities without costly ventilation upgrades.
This guide provides a practical, technically founded roadmap to marry electric lift equipment with structural storage for maximum throughput, minimum damage, and reduced operating cost.
1. Match equipment capability to your handling profile
Some of the important metrics to keep in mind when assessing equipment capabilities are:
- 2,500 kg at 600 mm nominal capacity at specified load center
- Battery Capacity (kWh) & Usable Runtime under your Duty Cycle
- Charging methodology – Opportunity charging vs. changeable battery swaps
- Drive speed and lift/lower cycle time
Sizing your fleet requires matching these specifications to the heaviest pallet and the highest shelving level. Also, consider diversifying the tasks heavier loads may need electric counterbalanced units; high racking often uses reach trucks. This all has to be kept in mind in any thorough strategy.
2. Structural storage design
Storage systems- racks-defines traffic patterns and affect which truck types are viable. The major structural racking options include: selective pallet racking, double-deep, drive-in/rack, push-back, and pallet flow. When designing, here are some things to keep in mind:
- Space beams according to pallet size and load-carrying patterns.
- Specify that the uprights and beams should have sufficient moment capacity and safety factor for dynamic impacts.
- Design working aisle widths in front of clear manufacturer minimums, plus operational clearance for turning and load swing.
- Structural racking increases usable vertical space, but requires tight interfacing with trucks. For very tall racking, check mast vertical reach plus operator visibility and required load backrest height.
3. Layout Sequencing
Sequence layout works to minimize travel distance the single largest component of forklift cycle time. Use these practical steps:
- Cluster high-turn SKUs near shipping/receiving to reduce travel.
- Duly utilize dedicated inbound/outbound lanes if volumes permit
- Configure staging lanes sized for pallet accumulation to avoid truck idle time.
- Use weight- and frequency-based slotting logic: heavier pallets lower, fast movers to the doors.
- Use simple spreadsheets or basic discrete-event models to simulate expected flows and estimate the truck-hours and required staging space. This will save many potential overbuilding of shelving or an under-sized electric forklift fleet.
4. Storage Tech Integration
In structural storages, electric trucks perform at their best when supplemented with low-lift automation. What should you be aware of?
- Gravity or powered pallet flow lanes minimize jogging of forklifts into deep racks.
- Automation must match your duty cycle and target for return on investment.
- At lower volumes, traditional racking with optimized electric forklifts is usually better. At higher throughput, added flow racks and shuttle systems bring big cuts in cycle time.
5. The middle-ground: shelving, safety, and durability
Whenever one introduces heavy duty shelving, the floor and racks can anticipate experiencing increased static and dynamic loads. Key considerations you must take into account:
- Anchor shelving to floor slabs with engineered anchor patterns. Provide seismic and load-code requirements accordingly.
- Specify beam-to-column connections with positive locking and labeled rated capacity visible at each bay.
- Design bays protection with guards (bollards) in high-traffic zones to reduce impact damage.
- Column protectors and face guards for the most exposed uprights.
Regular inspection and a documented rack inspection program will prevent progressive degradation resulting in sudden failures. After any replacement of beams, damage should be recorded with the actions taken to repair; re-label capacities
6. Battery management, charging pattern, and uptime
Electric fleets require a battery strategy that aligns with shift length and intensity. These include some types:
- Opportunity Charging: Quick charging during breaks to prolong runtime without needing to change the battery. Good for continuous operations with multiple chargers per bay.
- Battery swapping to achieve fast return-to-service with a second set of batteries appropriate for high-utilization sites where chargers are a bottleneck.
- Fast-charging with thermal management: increases battery stress; mitigate with temperature monitoring.
Monitor state of charge, amp-hour throughput, and temperature. Train operators on regenerative braking benefits and consistent lift/lower patterns that extend charge cycles.
7. Operator ergonomics, training and safety
Electric trucks have improved operator ergonomics-no vibration, smooth control. Provide standardized training for operators on the following:
- Limit lifting, control speed, and monitor load center
- Engagement procedures of the rack approaches speed, beam placement
- Safety of Battery Handling and Charging
- Incident reporting and near-miss documentation
Utilize telematics to monitor and enforce geo-fenced speed limits and log operator habits to enable coaching. Integrate performance KPIs with safety metrics.
8. Ensuring maintenance and lifecycle cost control
Track preventive maintenance on both trucks and racks. Important maintenance items which ensure the best possible ROI:
- Fork and heel deformity and wear examinations
- Mast chain tensioning and lubrication
- Brake and tire wear (solid vs. pneumatic options)
- Rack bolt torque checks and beam integrity
- Calculate TCO including energy cost, battery replacements, and rack repair.
Electrification often depicts a lower TCO due to the lower fuel and maintenance needs even when capital expenditure is higher.
Implementation Roadmap: A Summary of Concrete Steps
- Audit the flows and SKU profiles.
- Target throughput and peak loads are defined.
- Select racking types and check structural ratings.
- Define electric forklift classes and battery strategy.
- Pilot-run it in a production bay: Measure cycle times and damage incidents for a period of 30 days.
- Scale: With phased rollout, continuous feedback loops.
Conclusion
Streamlining appropriately sized Electric Forklift equipment with engineered storage and disciplined operations yields predictable throughput, less damage, and a safer work environment. Package data-driven slotting with proper shelving specification, battery strategy, and an emphasis on operator training and material handling turns from constraint to competitive advantage. Advanced material handling options such as considering even the intermittent use of an articulated fork lift can be part of the plan as your operation scales.