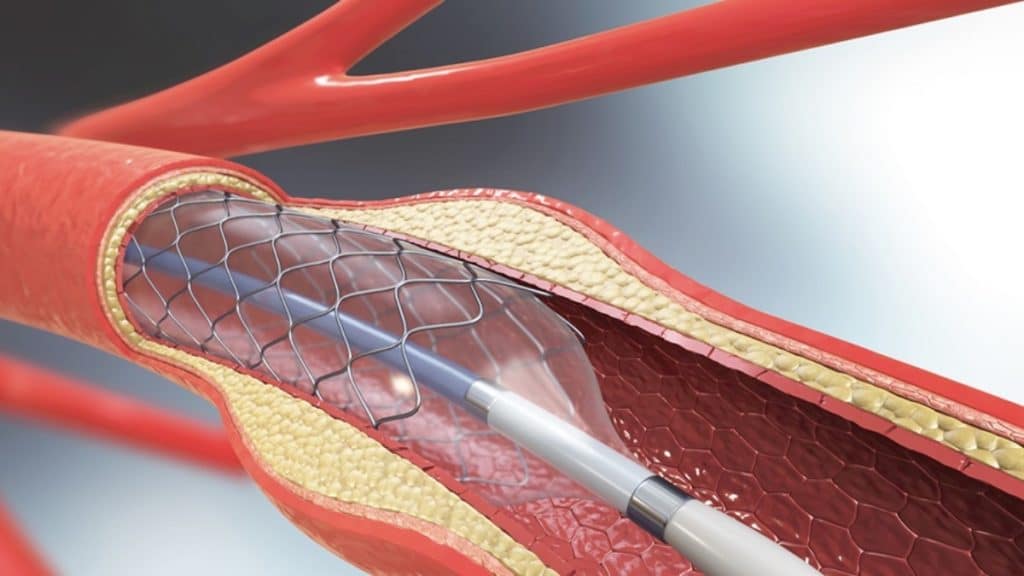
Nowadays, practically every angioplasty treatment uses a coronary stent. A thin, expanding coil of metal mesh is called a stent. It is inserted into the section of the artery that has just opened in order to prevent the artery from constricting or closing off.
An angioplasty is a procedure used to clear congested or clogged coronary arteries caused due to coronary artery disease. It restores blood flow to the heart muscle without requiring open heart surgery. Without requiring open cardiac surgery, it restores blood flow to the heart muscle. In a medical emergency, such as a heart attack, angioplasty may be carried out.
Coronary stents are now used in nearly all angioplasty procedures, which are small, metal mesh tubes that expand inside a coronary artery. A stent is often placed during or immediately after angioplasty. It helps prevent the artery from closing up again. A drug-eluting stent has medicine embedded in it that helps prevent the artery from closing in the long term.
Apollo offers the expertise of some of the best cardiologists in Bangalore[1] and all over India, who have experience in treating a wide range of cardiovascular conditions. You can opt for online consultations and physical doctor appointments that suit you the best, via Apollo 24|7.
What are Coronary Stents and Their Types?
Coronary stents (CS) are expandable tubular metallic implants that are inserted into coronary arteries with stenosis because of an underlying atherosclerotic condition. The treatment is known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary angioplasty with stent implantation. The coronary stent originally emerged in the 1980s, and its shape, structure, and material used, have evolved over time.
Types of Coronary Stents
- Bare metal stents (BMS): These are simple metal mesh tubes, which can be used in both the coronary and carotid arteries.
- Drug-eluting stents (DES): These are the most common types of stents that are used in the coronary arteries. DES comprises three components — a metallic stent platform, an active pharmacological drug agent, as well as a carrier vehicle. Stainless steel or cobalt-chromium are the most common metals and give long-term mechanical stability to counteract vascular recoil.
- Drug-eluting balloons (DEB): This type of stent simply contains an antiproliferative drug coating and no underlying metallic structure of the stent.
- Bioresorbable scaffold system (BRS): BRS lacks a metallic structure and is completely resorbed after performing its purpose.
Other stents, such as bifurcation stents and covered stents, have been designed for specific applications such as lesions over a vascular bifurcation or coronary artery perforation.
How is the Process Done?
- Before the commencement of the angioplasty procedure, the patient will be given some pain medicine. The person may also be provided with medicine that will give relaxation, and also blood-thinning medicines to prevent a blood clot from forming.
- The patient will be lying down on a padded table. The medical expert will insert a flexible tube (catheter) into an artery. Sometimes the catheter will be placed in the wrist or arm, or in the upper leg (groin) region. During the procedure, the patient will stay awake.
- The medical professional will then carefully guide the catheter up into the heart and arteries with the help of real-time X-ray images. The body will be given an injection of liquid contrast, also known as “dye,” to show how blood flows through the arteries. This makes any blockages in the blood arteries leading to the patient’s heart easier to observe for the doctor.
- A guide wire is used to cross the blockage. A balloon catheter navigated over the guide wire and into the blockage. The balloon in the end is inflated. This opens the clogged vessel, restoring appropriate blood flow to the heart.
- This blocked region may subsequently be surgically placed with the wire mesh tube (stent). The balloon catheter is implanted together with the stent. When the balloon is inflated, it grows. To assist in keeping the artery open, the stent is kept in place.
- Almost always, a drug is applied to the stent (referred to as a drug-eluting stent). This kind of stent might lessen the likelihood that the artery would eventually close again in the future.
Conclusion
Angioplasty is done to improvise blood flow to the coronary arteries. When the constricted artery is in a location that is accessible in this way, this is exactly what is done. Angioplasty is not a treatment option for every case of coronary artery disease (CAD). Depending on your situation, your healthcare professional will choose the best course of action for treating your CAD.
Apollo Hospital Bangalore[2] is a renowned cardiac hospital in the city, known for its treatment and patient care excellence. Apollo Hospitals is here to provide you with the best cardiology treatments in Bangalore. We work with a team of well-known, award-winning, and best cardiologists in Bangalore who have years of expertise in diagnosing, investigating, and treating acute and chronic cardiac conditions. Get the most precise assessment of your cardiac disease, as well as a detailed look at its therapy and management.
References
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007473.htm#:~:text=A%20coronary%20artery%20stent%20is,closing%20in%20the%20long%20term.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/angioplasty-and-stent-placement-for-the-heart
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507804/ https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/stents#:~:text=Stents%20can%20be%20made%20of,arteries%20such%20as%20the%20aorta.